
As energy storage adoption continues to grow in the US one big factor must be considered when providing property owners with the performance capabilities of solar panels, inverters, and the batteries that are coupled with them. That factor is temperature. Temperature, both hot and cold, can have a significant effect on the lifecycle, depth of discharge (DOD), performance, and safety capabilities of solar storage systems. Due to recent weather events, now is the time to learn all you can about how temperature can affect a battery when designing energy storage systems for your customers.
In the last couple of weeks, there have been record temperatures recorded throughout the US. In the month of July seven states recorded their warmest July since they’ve been keeping track over the past 126 years. In California’s Death Valley they reportedly hit 130 degrees Fahrenheit on August 16th, 2020, which, if true, is believed to be the hottest temperature ever recorded on the planet. But heat isn’t the only factor to think about, in May of 2020 it snowed in the Northeast region of the US! Far past the traditional end of winter. Due to the prevalence of these odd temperature swings, it’s important to factor in the effects that extreme heat and cold temperatures have on battery performance and to work solutions for these issues into your design.
As mentioned above the main capabilities of batteries that are affected by temperature are performance, lifespan, and safety. However, the way that these metrics are affected depends on the temperature, high heat changes a battery in different ways than if it was very cold. First, let us focus on how high temperatures can affect battery performance.
Effects of Heat
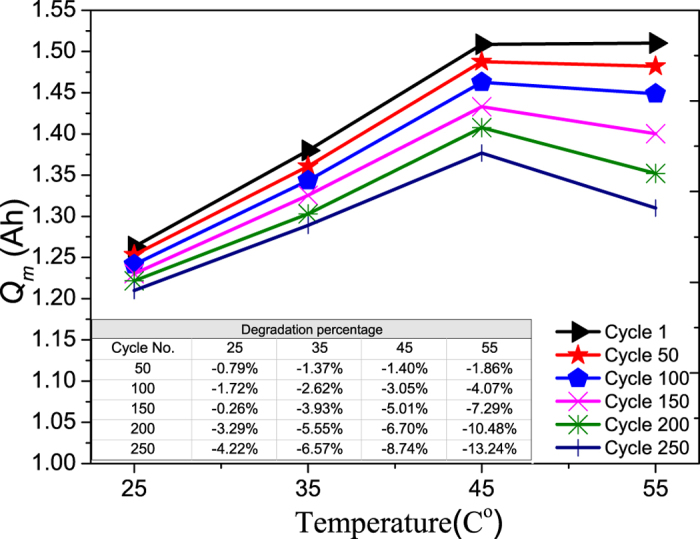
When temperatures increase this affects the chemical reactions that occur inside a battery. As the temperature of the battery increases the chemical reactions inside the battery also quicken. At higher temperatures one of the effects on lithium-ion batteries’ is greater performance and increased storage capacity of the battery. A study by Scientific Reports found that an increase in temperature from 77 degrees Fahrenheit to 113 degrees Fahrenheit led to a 20% increase in maximum storage capacity. However there is a side effect to this increased performance, the lifecycle of the battery is decreased over time. In that same study, it was found that when the battery is charged at 113 degrees versus 77 the lifecycle degradation was much more significant at the higher temperature. For the first 200 cycles the battery performance only degraded 3.3% at 77 degrees; at 113 degrees the performance decreased by 6.7%. That’s more than double the amount of degradation! Based on the greater degradation at higher temperatures, the battery lifecycle can be severely diminished due to consistent exposure to extreme heat. While heat exposure does temporarily increase battery capacity the damage that it does to the lifecycle can cause long term problems and prolonged heat exposure should be avoided.
Effects of Cold
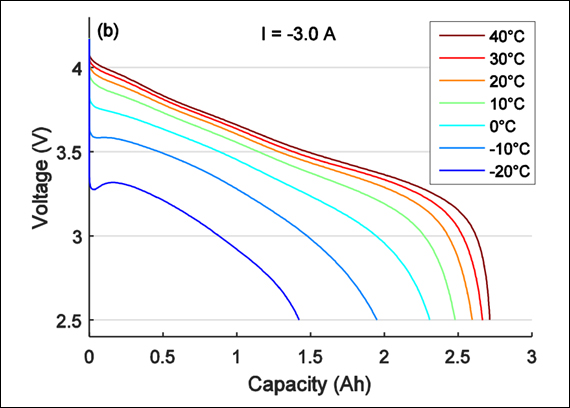
Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures also has a big impact on battery performance and safety. When temperatures drop the internal resistance of the battery is increased. This means that it requires more effort by the battery to charge, in turn lowering the capacity. However, it is important to note that the loss of capacity also depends on the charge and discharge rates and the effect of the cold weather is different for batteries made with different chemistries. For example, a lead-acid battery may provide just half the nominal capacity at 0° F.
The operating temperatures of batteries are also different based on the type of battery you are working with. For example, lithium-ion batteries can be charged from 32°F to 113°F and discharged from –4°F to 140°F (however if you operate at such high-temperature levels you do run into the problems mentioned earlier). But Lead-acid batteries can be charged and discharged from -4°F to 122°F. It’s very important to be aware of the charging temperatures that a battery can accommodate. If batteries don’t operate at the accepted temperature, charge acceptance will be decreased because ion combination will be slower. Forcing high current can build up pressure causing explosions of sealed batteries.
When talking to customers about the capabilities of batteries it’s critical to understand all factors that can have an impact. Hot or cold temperatures both have different but impactful effects and it’s important to be able to give property owners the information that they need to make an informed decision for their system.


Comments
It would be useful to know the effects of temperature on the lifetime (cycles) of a battery. Capacity is not the only important factor to consider.
Thank you for your comment. While heat exposure does temporarily increase battery capacity the damage that it does to the lifecycle can cause long-term problems and prolonged heat exposure. This should be avoided.(Chart above shows degradation percentage in reference to temperature over cycle numbers)
whos the publishers its for my science fair
Thank you for your comment. This article was originally written in 2020 and the data was pulled from an article in PV Magazine's US edition.
dear sir, hank you very much for this very important informations
You're welcome. Thank you. So happy to hear that it was helpful.
Which would last the longest between a 10 degree 25 degree and 30 degree celsius battery
It depends on the battery chemistry and the battery warrantee. All batteries are different, but pretty much every battery you would use for a typical solar installation is designed around the 25 degree temperature that humans also feel comfortable at.
If you ran a battery at 10 degrees you would have the slowest chemical reactions of the three temperatures - but to make it last longer than the other two batteries, you'd need to limit current to avoid raising the internal temperature.
Simply put, if you want your battery to last a long time, read the warrantee, not the spec sheet. That will tell you the ideal temperature, depth of discharge and current (C) rate. Thanks again for your comment.
I have been doing a science project recently and I tested battery capacity at 30ºC, 20, 10, and 0 degrees. The capacity was highest at 30 then 20 etc. Why would the capacity be higher at higher temperatures if the reaction rate is also higher at higher temperatures. Is there another factor I am unaware of? Thanks